Algo trading, short for algorithmic trading, has completely transformed the way buying and selling take place in the stock market. Gone are the days of shouting on trading floors or making phone calls to place orders. Today, traders uses software programs capable of executing hundreds of trades within seconds. These programs follow a predefined set of rules, known as algorithms to determine when and what to trade. Algo trading is no longer just a passing trend; it is a technological advancement that has become a vital part of global financial markets. In this blog, we will explore the history of algo trading, how it works, its advantages and risks, its journey in India, and the promising future it holds.
The Birth of Algo Trading: From Paper to Programs
 The journey of algo trading began in the 1970s, when stock exchanges started shifting from manual systems to electronic ones. Before that, traders would physically meet at the stock exchange to buy and sell shares. But with the birth of NASDAQ in 1971 ,the first electronic stock exchange, things began to change.
The journey of algo trading began in the 1970s, when stock exchanges started shifting from manual systems to electronic ones. Before that, traders would physically meet at the stock exchange to buy and sell shares. But with the birth of NASDAQ in 1971 ,the first electronic stock exchange, things began to change.
By the 1980s, large institutions developed programs that could execute bulk trades quickly and without emotional interference. These were basic forms of algorithmic trading, also known as program trading. The goal was simple to split large orders into smaller ones and execute them smoothly without affecting stock prices drastically. This was the seed that would later grow into today’s powerful algo trading systems.
Read More: Institutional Investors : The Key Players Behind Stock Market
The Rise of High-Frequency Trading (HFT)

The real boom in algo trading happened in the early 2000s, when high-frequency trading (HFT) took center stage. With faster internet, powerful computers, and better financial data, traders began to write complex algorithms that could make thousands of trades in microseconds.
These high-speed strategies gave rise to a new type of trading, one that relied on speed, volume, and precision. Traders could make profits on very small price changes, but do it hundreds or thousands of times a day. In the U.S., by 2010, over 60% of the trading volume came from algo-based systems. But as speed increased, so did the risks and this became clear during a shocking event.
Flash Crash of 2010: A Wake-Up Call
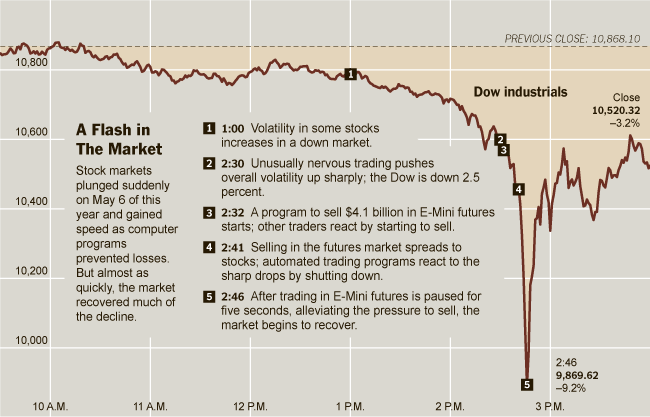
On May 6, 2010, the U.S. stock market witnessed a terrifying incident, the Flash Crash. In just a few minutes, the Dow Jones index fell by nearly 1000 points, wiping out billions of dollars, before recovering just as quickly. Investigations showed that a large trade triggered a chain reaction among algorithms. Panic spread across automated systems, and they started selling rapidly, deepening the crash. No human was fast enough to stop it.
This incident made regulators and market participants aware of the dangers of unchecked algo trading. As a result, strict rules, testing environments, and “circuit breakers” (automatic halts during rapid falls) were introduced.
Read More: Beginner Blunders in Share Market
Algo Trading in India: A Growing Force
 India joined the algorithmic trading race in 2008, when the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) allowed Direct Market Access (DMA). This allowed brokers to use their own trading software to access stock exchanges without manual involvement.
India joined the algorithmic trading race in 2008, when the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) allowed Direct Market Access (DMA). This allowed brokers to use their own trading software to access stock exchanges without manual involvement.
At first, algo trading in India was only for big institutions like banks and mutual funds. But soon, with the rise of fintech platforms and Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), even small traders and retail investors began using automated strategies.
Today, around 50% of the trades on the NSE (National Stock Exchange) happen through algorithmic systems. India’s growth in this space is being fueled by:
- Faster internet
- Cheaper data
- Smarter retail investors
- API access from platforms like Zerodha, Upstox, and Alice Blue
How Algo Trading Works
So, how does algo trading actually work?
It starts with a trading strategy, for example:
- Buy a stock if its 50-day moving average crosses the 200-day average.
- Sell a stock if RSI (Relative Strength Index) crosses 70.
These rules are coded into a program using languages like Python, Java, or R. The software is then connected to a broker’s API to access live market data and place trades automatically.
Types of algo trading strategies include:
- Trend-following: Based on indicators like moving averages, momentum, and breakouts.
- Mean-reversion: Based on the belief that prices return to the average.
- Arbitrage: Exploiting price differences between markets.
- Market-making: Constantly buying and selling to provide liquidity.
Benefits of Algo Trading
The popularity of algo trading comes from its many benefits:
- ✅ Speed: Algorithms can place orders in milliseconds which is much faster than any human.
- ✅ Accuracy: No typing errors or delayed decisions.
- ✅ Emotion-free: No fear or greed, just logic and data.
- ✅ Backtesting: Strategies can be tested on past data to check their success rate.
- ✅ Scalability: One system can manage multiple strategies across many markets.
For both institutions and individual traders, algo trading brings consistency and efficiency.
Risks and Challenges in Algo Trading
However, algo trading is not without its risks:
- ⚠️ System errors: A small bug in the code can cause huge losses.
- ⚠️ Overfitting: Strategies may perform well on past data but fail in real markets.
- ⚠️ Market crashes: Algorithms may create feedback loops during panic conditions.
- ⚠️ Unfair access: Firms with better technology may have an edge over others.
To tackle these issues, SEBI in India has issued strict norms. Algorithms must be approved, tested in live environments, and monitored regularly. Brokers are also responsible for the actions of their clients’ algorithms.
Role of AI and Machine Learning in Algo Trading
 The next stage in algo trading is here: Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML).
The next stage in algo trading is here: Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML).
Unlike traditional algorithms that follow fixed rules, AI-based systems can learn from market data, improve over time, and adapt to new situations. For example:
- They can analyze Twitter sentiment and news headlines.
- They can detect patterns in price charts that human eyes may miss.
- They can reduce false signals and make smarter decisions.
Some hedge funds and institutional investors already use AI-driven models to stay ahead. In the future, retail traders may also get access to these tools as they become more affordable.
The Future of Algo Trading

The future of algo trading looks bright and inclusive. As more people become financially aware, they want smart, automated tools to manage their investments. Platforms now offer drag-and-drop strategy builders, pre-built bots, and educational content to make algo trading easy for everyone.
In India, initiatives like Digital India, affordable smartphones, and fintech education will bring even small-town traders into the algo world.
We may also see:
- Cloud-based trading platforms
- Voice-command-based trading systems
- Blockchain integration for secure trade tracking
- And eventually, quantum computing, which may take algo trading to unimaginable levels.
But with these advancements, ethical trading and transparency must remain key. Tech should empower all, not just the privileged few.
Final Thoughts
Algo trading is not just for experts anymore. With a bit of learning and the right tools, even beginner investors can benefit from automated strategies. Whether you want to avoid emotional decisions, save time, or trade more efficiently, algorithms can be your best friend in the market. But remember that automation doesn’t guarantee profits. It’s still important to learn, test, and trade responsibly.